Deep Dream Artificial Intelligence – the content:
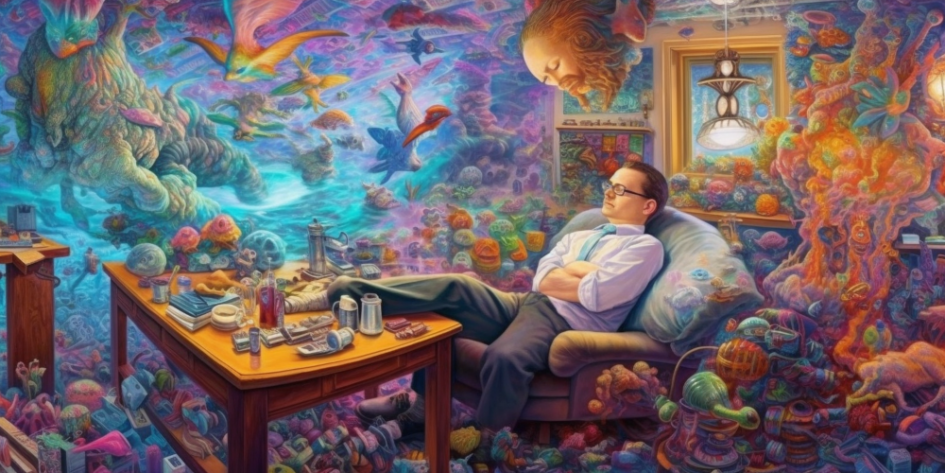
DeepDream is a computer vision program that uses a convolutional neural network to find and enhance patterns in images via algorithmic pareidolia. It was created by Google engineer Alexander Mordvintsev and was developed for the ImageNet Large-Scale Visual Recognition Challenge in 2014. The program popularized the term (deep) “dreaming” to refer to the generation of images that produce desired activations in a trained deep network, and the term now refers to a collection of related approaches.
Generator/Outcomes: https://deepdreamgenerator.com
On Github: https://github.com/google/deepdream
History
The DeepDream software originated in a deep convolutional network codenamed “Inception” after the film of the same name. The dreaming idea and name became popular on the internet in 2015 thanks to Google’s DeepDream program. The idea dates from early in the history of neural networks, and similar methods have been used to synthesize visual textures. Related visualization ideas were developed (before Google’s work) by several research groups. After Google published its techniques and made its code open-source, several tools in the form of web services, mobile applications, and desktop software appeared on the market to enable users to transform their photos.
The DeepDream model has also been demonstrated to have applications in the field of art history. It has been used to generate vivid, dreamlike images that resemble famous paintings, such as Vincent van Gogh’s “Starry Night.” This has led to speculation that the neural network is capable of learning the styles of different artists and reproducing them in its unique way.
The dreaming idea can be applied to hidden (internal) neurons other than those in the output, which allows exploration of the roles and representations of various parts of the network. It is also possible to optimize the input to satisfy either a single neuron (this usage is sometimes called Activity Maximization) or an entire layer of neurons. While dreaming is most often used for visualizing networks or producing computer art, it has recently been proposed that adding “dreamed” inputs to the training set can improve training times for abstractions in Computer Science.
Hallucination Machine
DeepDream has been used to create a hallucination machine, which applies the DeepDream algorithm to a pre-recorded panoramic video, allowing users to explore virtual reality environments to mimic the experience of psychoactive substances and/or psychopathological conditions. In 2017, a research group out of the University of Sussex created a Hallucination Machine, applying the DeepDream algorithm to a pre-recorded panoramic video, allowing users to explore virtual reality environments to mimic the experience of psychoactive substances and/or psychopathological conditions. They were able to demonstrate that the subjective experiences induced by the Hallucination Machine differed significantly from control (non-‘hallucinogenic’) videos while bearing phenomenological similarities to the psychedelic state (following administration of psilocybin).
In 2021, a study published in the journal Entropy demonstrated the similarity between DeepDream and actual psychedelic experience with neuroscientific evidence. The authors recorded the Electroencephalography (EEG) of human participants during the passive vision of a movie clip and its DeepDream-generated counterpart. They found that DeepDream video triggered a higher entropy in the EEG signal and a higher level of functional connectivity between brain areas, both well-known biomarkers of the actual psychedelic experience. In 2022, a research group coordinated by the University of Trento measured participants’ cognitive flexibility and creativity after exposure to virtual reality panoramic videos and their hallucinatory-like counterparts generated by the DeepDream algorithm. Following the simulated psychedelic exposure, individuals exhibited an attenuated contribution of the automatic process and chaotic dynamics underlying their decision processes, presumably due to a reorganization in the cognitive dynamics that facilitates the exploration of uncommon decision strategies and inhibits automated choices.
Conclusion
DeepDream is a computer vision program that uses a convolutional neural network to find and enhance patterns in images via algorithmic pareidolia. The program popularized the term (deep) “dreaming” to refer to the generation of images that produce desired activations in a trained deep network, and the term now refers to a collection of related approaches. DeepDream has been used to create vivid, dreamlike images that resemble famous paintings and to explore the roles and representations of various parts of the network. It has also been used to create a hallucination machine, which applies the DeepDream algorithm to a pre-recorded panoramic video, allowing users to explore virtual reality environments to mimic the experience of psychoactive substances and/or psychopathological conditions. While DeepDream is most often used for visualizing networks or producing computer art, it has recently been proposed that adding “dreamed” inputs to the training set can improve training times for abstractions in Computer Science.
Video
Do you have an interesting AI tool that you want to showcase?
Get your tool published in our AI Tools Directory, and get found by thousands of people every month.
List your tool now!